How to Read Anacronyms for Radio Ta;k

There are many terms and phrases used in the radio industry today. For example, exercise yous know what CEF, Ramp, or Feedback mean? If non, we're going to explain these along with some other most common radio terms and phrases in this comprehensive radio glossary.
Looking for a particular term? Find it by pressing CMD+F (Mac) or CTRL+F (Windows) and entering your term. If we missed any technical words, jargon, or abbreviations used in the broadcasting manufacture, then allow usa know in the comments.
Accapella
Function of a jingle that is fabricated upwardly of voices without any music.
Ad
Advertizing is an abbreviation for an advertisement. Usually, it'due south a recorded piece of sound to promote a business or event.
A-D Converter
A-D converter is curt for Analogue to Digital Converter. It changes a constant electrical betoken into a stream of binary numbers like 1' and 0's. These are normally found in estimator soundcard, minidisks, and CD recorders.
Extemporaneous
Ad-lib or Ad-libbing is when a presenter improvises. Unremarkably, when something goes wrong, like the evidence is disturbed or theirs a technical fault.
Alexa Skill
Smart devices, like the Amazon Echo, let broadcasters create an Alexa skill and so listeners can tune in at home or work via phonation control.

Counterpart Betoken
Analogue recording equipment records the exact waveform of the original sound. It converts an electrical indicate from the mi and back into the air movement at the speaker.
Attenuate
Reduces the intensity of a audio signal, much like a volume control dial.
Sound Engineering Society / European Broadcast Wedlock (AES/EBU)
AES/EBU is a body of digital audio transfer standards, for example, they brand sure microphone XLR connectors are 3 pins.
Automatic Gain Control (AGC)
AGC adjusts the book to compensate for the level. It helps reduce dissonance when a presenter gets too loud, for example, when they shout or become up close to the microphone.
Automation
Software or equipment similar mixers and soundboards loaded with pre-set sound to automate shows. Often these sounds are controlled by a computer to ensure authentic and repeatable audio. For example, Radio.co has tags. Tags allow yous to randomise playlists without manually selecting tracks.
Auxiliary Input (Return)
The road back into a sound desk for a line-level indicate sent to a piece of outboard equipment via an auxiliary send.
Auxiliary Output (Transport)
Line level output from a sound desk which can exist used for foldback or monitoring without cross over to the main output.
Average Weekly Hours Per Listener
Full hours of listeners tuned into your station averaged across the total relevant population. This is calculated past dividing the weekly hours by the full population for your audience.
Back Denote
Back announcing is when a presenter talks most a vocal that has just played.
Back Time
Back timing is the technique of working out how much time is left before an event. For example, if a DJ's bear witness is going to finish, they work out the correct length of a song to ensure they don't terminate too early on or overrun.
Balanced Line
Reduce interference carrying a line by using a third usher similar a shield. Balanced lines are less prone than unbalanced for interference. One of the bespeak wires carries the audio signal, while the other carries an out-of-phase inverted duplicate. When the signal reaches the destination, the inverted indistinguishable is flipped and added to the original. Whatever noise added by interference is also inverted. When combined with the non-inverted noise, the two noise signals cancel each other out.
Bandwidth
In terrestrial radio, bandwidth is the range of the broadcasting equipment. In internet radio, bandwidth is the amount of data consumed by listeners. Piece of work out how much bandwidth you use on your radio station with the Internet Radio Bandwidth Calculator.
Bass
Bass is the lower cease of the music scale at around 60 to 250 Hz. For case, a male voice ranges from 85 to 180 Hz, whereas a female voice is from 165 to 255 Hz.
Bed
Audio that is used to talk over by the DJ. Usually, it'southward function of a jingle or segment between tracks to keep a flow.
Bus
A bus is a single line in a mixing desk that can receive signals from a number of sources like a microphone and CD player. The passenger vehicle carries the line to the master audio channel to output to a destination.
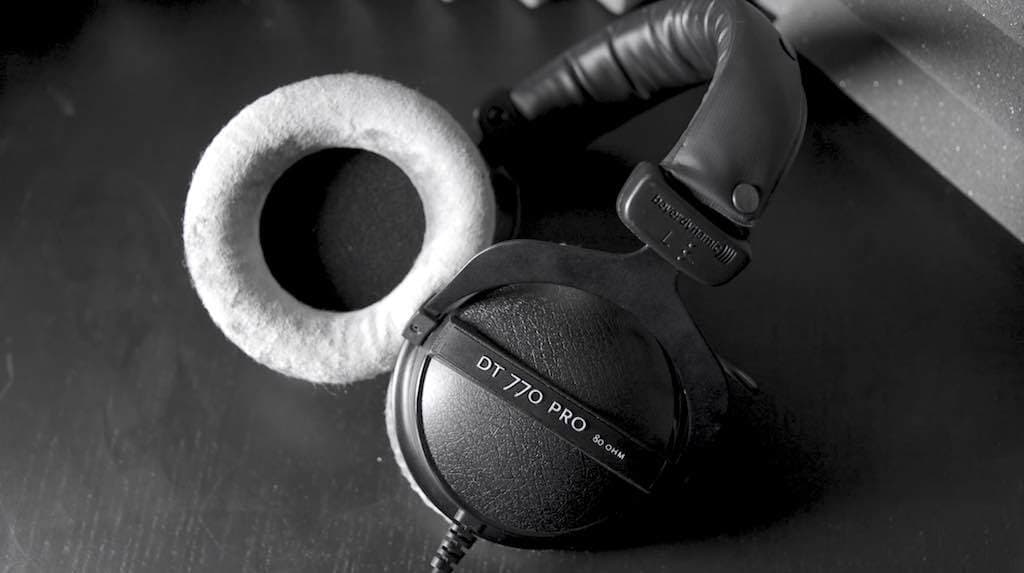
Cans
Headphones are commonly referred to in the radio industry as cans, just like the Beyerdynamic DT770 Pro headphones.

Cart
Carts or "tapes" were used to tape jingles and ads.
Clean Feed
Also known as a mix-minus, is an sound signal sent from your mixer that includes everything except designated inputs.
Meaty Disk (CD)
CDs store audio recordings. Some radio stations all the same utilize these as role of their setup.
Compressor
Compress audio to reduce its dynamic range (the difference between the loudest and quietest parts of a track), mainly washed to increase the overall book.
Commercial Production (Com Prod)
A section in a radio station that produces commercials and adverts.
Cost Efficiency Factor (CEF)
Toll of reaching out to 1,000 people in your target audience. For example, what is the price of reaching 1,000 of your listeners with simply one advert? Cost per one,000 compares the efficiency and value by different stations.
Crosstalk
Unwanted leakage of point from one channel to another.
Cue
Cue is the offset of a rail. Information technology's ofttimes used as a remark to set up earlier starting something, for example, a presenter nearly to do a live show.
Cue Light
Signal to the presenter that she/he tin starting time dissemination or to stand up by, e.g. red light usually means standby, greenish light means go.
Cut
Cuts are small segments in a radio show. For instance, news stations take modest reports similar bulletins.
Day Parts
Day parts mean the different times of the day y'all can run an ad campaign. Two major days parts on the radio are for morning time shows (commonly 6am-9am) and evening shows (4pm-7pm).
Delay Unit
A device used to delay a show before it broadcasts, normally used during phone calls every bit a style to cut offensive language earlier it transmits.
Demo Tape
Demo tapes, or "airchecks" as it was once known, are pieces of audio showcasing a new runway from a band or presentation techniques from a DJ.
Digital Audio Tape (DAT)
A DAT, frequently mistaken for cassette tapes due to their similar appearance, is a device to store audio recordings.
Deutscher Industrie Normen (DIN)
DIN is a European standard roofing audio connectors, ports, and tape equalisation characteristics.
Disc Jockey (DJ)
A person that plays tracks. Unremarkably segueing between, introducing songs, and providing insight or facts.

Distortion
An audio point sound quality does non sound expert. Usually acquired by equipment overloading or wrong setup.
Donut
A jingle that starts with singing, music in the heart, and singing again at the end.
Dubbing
Copying sounds from one medium to another. For example, when an English film is exported to a non-English language speaking audience then the video is kept, but the audio is replaced. Effectively the original audio gets dubbed over by new actors.
Equalisation
Adjusting the tonal quality of the audio. Commonly, music tracks are equalised to smooth out the audio levels so it's clearer to listen to.
Fade In
The sound level of a track gradually becomes louder until it reaches its proper level. Commonly fade-ins are used for smoother transitions to segue into a new rail or DJ segment.
Fade Out
The sound level of a track gradually becomes quieter until it disappears altogether. Normally fade-outs are used for smoother transitions to segue into a new runway or DJ segment.
Fader
A sliding dial on a mixing desk to command the audio levels like the Axia iQ Mixing Panel.
Feed
A signal from one device to another, for case, 2 presenters with two microphones take two feeds. Feed is too referred to as a ability supply for a piece of equipment similar a mixer.
Feedback
Feedback, sometimes chosen Howlround, is a rumbling or whistling noise caused by a sound system. Loud environments tend to have feedback as audio is picked up from a speaker through a microphone.
Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN)
A loftier-quality line used to transmit information like a voice or video.
Intro
The starting time of a song, usually before the vocals.
Frequency
The number of times your ad campaign is heard by your listeners over a certain period of time.
Gross Rating Points (GRPs)
GRPs are the gross OTH (explained further down) of a campaign equally a percentage of your target market. One rating point equals 1% of the population. For example, a gross OTH of 200,000 for a target market of 50,000 listeners, this would generate 400 GRPs. This is worked out past multiplying OTH by the weekly achieve percentage (besides explained further down).
Impacts
Impacts are the gross number of opportunities listener have to hear an advertizement. One impact is one person'due south listening to one spot. These are added together to requite total impacts for an ad campaign or total impacts for all the commercial airtime on your station. Ultimately, this is calculated by multiplying OTH by the weekly reach.
Jack
A jack is a type of plug institute on the end of cables. Jacks come in different sizes, most commonly 2.5mm, 3.5mm and quarter inch. They tin can exist mono or stereo and balanced or unbalanced. Most professional equipment uses counterbalanced jacks.
Jackfield
A jackfield, or patchbay in the UK, is used to re-route audio to different equipment, much like a junction box.
Jingle
A brusque audio clip played on a radio evidence used for promotion. Sponsors or advertisers employ jingles between tracks, normally accompanied past voice-overs and sound furnishings to engage listeners.
Limiter
An audio cap to limit the volume level in instance it gets likewise high. High volumes tend to distort the stream and impairment equipment.
Line Level Bespeak
A standard audio level for both inputs and outputs to keep sound at an boilerplate level.
Line-upwards Tone
A signal frequency or level used for setting up equipment sound levels. For example, adjusting multiple microphone volume levels so they all match.
Link
Links are sandwiched in between songs, usually featuring info near what'south upwardly adjacent, news, or competitions.
Listener Requests
Take rail requests from listeners. Streamline the process past automatically taking requests and playing them out on your station.

Logging
Record a radio station's entire output. Commonly used for licensing purposes to log tracks. Online stations with Radio.co log tracks and more using reports.
Market Share
Scrap of an onetime school term nowadays. Just market share used to mean the per centum of all radio listening hours within your broadcasting area, typically in terrestrial radio like AM, FM, or DAB.
MiniDisc (MD)
Remember these? They were a device used to store sound recordings, much like a compact disc. Back in the early 00's, radio studios were using them in total swing - any happened to minidiscs?!

Mic
Mic is an abbreviation for a microphone, used by the DJ to talk into.
Mixdown
A mixdown contains multiple tracks, ofttimes counterbalanced (so it sounds skilful, not as well loud or too quiet) and fix for playback.
Mixer
A mixer is a panel desk with several inputs for sound equipment. Each input is a channel, outputting into one principal channel, and finally to a calculator or device to broadcast. Check out the Best Dissemination Desks You Should Know.
Monophonic (MONO)
An audio signal that but comes from one source, or aqueduct. When played through stereo systems, the signal will be split evenly between the left and correct channels.
News Bulletins
Broadcast a hosted news feed, on the hour, to all your listeners automatically. Only without the need for scheduling events or replacing files.

Opportunity To Hear (OTH)
OTH represents how many times a listener is about likely to hear your ad.
Exterior Circulate (OB)
A radio show broadcast exterior, just like we did hither Taking Shows on the Road.
Over Running
When a track or DJ exceeds the expected finish fourth dimension.
Peak Programme Meter (PPM)
PPM used on audio equipment to show how loud sound levels are.
Phantom Ability
Most condenser microphones require a stronger ability supply of 48v to work. Phantom power sends this voltage through the aforementioned cable as the audio bespeak. About mixers will exist equipped with 48v phantom power to accommodate condenser microphones.
Phase
Soundwaves move in repetitive cycles. When two soundwaves of the aforementioned frequency synchronise with one another they will double the amplitude, this is known equally being 'in phase'. If synchronised when the soundwaves are shifted 180 degrees out of phase of each other, the sound waves will cancel each other out and produce no sound.
Population
The number of people who live inside the TSA (explained further down) of your station.
Pre-Fade Heed (PFL)
Control the sound through a mixing desk-bound to listen to an sound stream without actually broadcasting the signal. Can exist used to check the sound quality and find faults.
Pre-Fade
An output from a desk that is independent of the aqueduct fader.
Pre-Record
Recording an sound stream earlier officially dissemination to listeners.
Program Controller (PC)
The person in charge of content broadcast on a radio show.
Programme Director (PD)
Like to a programme controller, they manage radio shows to make sure they are running smoothly.
Promo
Curt for promotion, a promo is a form of advertising.
Q Carte du jour
A written piece for the presenter to read. These are like cliff notes to brand sure shows keep on rails.
Racks
Storage for all the radio station's equipment.
Radio Frequency (RF)
A signal for which an AM/FM radio station is broadcast on, like 109.5FM.
RAJAR
RAJAR stands for Radio Joint Audience Research. It is a unmarried audience measurement system for the U.k. radio industry servicing the BBC and commercial radio stations.
Ramp
The level of the audio increasing. Used when a presenter has finished talking segue into a track.
Reach Alphabetize
Reach alphabetize is the weekly accomplish percentage of a station against a target marketplace indexed confronting the all developed weekly accomplish per centum of your station. Basically, it indicates whether a target marketplace is more or less likely to heed to your station.
Relay
Stream other stations on your own - platonic for affiliated shows or networks.
Riding the Fader
A technique to manually control the fader to optimise the volume level, similar minimising feedback and background dissonance.
Script
A written piece for the presenter to read during the prove. Use this method by following the Top five Tips to Writing Awesome Radio Scripts.
Segue
A term used to draw the transition from one track to some other. Ofttimes, presenters volition introduce the next runway or talk most what's to come during the prove, which is a method of segueing.
Share Index
Share index is the market share percent of your station confronting the target market place indexed against the all adult weekly reach percentage of your station. It indicates whether a target market is more or less likely to listen to your station. Much like the accomplish index.
Sibilance
Sounds similar S, SH, or CH are emphasised. For example, saying the following may misconstrue the audio during a prove: silly sausages shaking chorizo slices.
Signal to Dissonance Ratio
The ratio of the average betoken to the background dissonance.
Splice
To join or edit audio together. Splicing used to involve physically bonding tape together. Now it means to join different audio files into 1.
Audio Effects (SFX)
Noises played during shows to add a layer of inventiveness, like automobile horns, lightning, and footsteps.
Sweeper
A branded radio station jingle played between two tracks.
TalkBack
A fashion to talk to the studio whilst on location without it beingness circulate. It's also a style for ii studios to communicate without having to go dorsum and forth.
Talk Show
Invite guests to participate in talk shows which can be saved to your station for later dissemination.
Technical Operator (T/O)
Somebody who works in a radio station managing the technical side of the operation. T/O likewise stands for Talk Over, when a presenter volition talk over faded down music.
Full Survey Surface area (TSA)
The TSA is the area within which your station's audience is measured. This is commonly known as the station'due south total survey area or manual area, oftentimes relating to terrestrial broadcasting like FM/AM transmissions.
Full Time Spent Listening
Runway your station's functioning by seeing how long your listeners have been tuned in for on a specific day.

Total Weekly Hours
Total weekly hours are the total number of hours that your station has been listened to over the course of a calendar week. This is the sum of all quarter-hours for all listeners.
Full Weekly Accomplish
Weekly reach is the number of listeners who tune into your station within at least 1 quarter-hr period during a week.
Twig
Twig is another name for an aerial, something used to accept incoming or outgoing broadcasting transmissions.
TX
TX is another proper name for transmission, which is how audio is broadcast to the listener.
Ultra-High Frequency Link (UHF Link)
A radio signal used to transmit audio from one location to another.
Phonation Tracker
Record audio snippets to sandwich between automated shows. Voice tracking lets you record and add on the fly, like covering breaking news, advertizing hoc promos, or quick announcements.

Volume Unit of measurement (VU)
Used on audio equipment to show a rails'southward loudness.
Wavelength
The distance from one signal on a vibrating wave to the aforementioned point on the side by side wave.
Weekly Reach %
The weekly reach expressed as a percentage of the population within the TSA.
XLR
A three-pivot connector for sound equipment. Created in California just standardised by the Great britain, an XLR cable is commonly used with microphones and other audio devices as information technology is the standard connector for counterbalanced connections.
Radio Glossary
That's it for the radio glossary. Hopefully, nigh of the common radio terms and phrases have been covered. If nosotros've missed a few then let united states of america know in the comments.
Source: https://radio.co/blog/radio-glossary-terms-phrases-explained
0 Response to "How to Read Anacronyms for Radio Ta;k"
Post a Comment